Categories
- Pipe & Tube (18)
- Flange & Fitting (97)
- Fastener & Gasket (12)
- Valve & Pump (18)
- Base Material (11)
- Equipment (8)
- Application (30)
- Technical (110)
A swage nipple, also known as a swaged nipple, is a short piece of pipe used to make reductions in the straight-run line and create a smooth transition from a larger to a smaller diameter in the nipple. The term “swage” refers to the process of reducing the diameter of one end of the nipple by hammering or squeezing, which results in a permanent deformation to achieve a desired size and shape. The swage nipples can be manufactured in accordance with a series of international standards such as MSS SP 95, BS 3799, and SH/T 3419. They can be classified as concentric type (having a common centerline) and eccentric type (having offset centerlines). The concentric swage nipple maintains the same centerline at both the large and small ends of the fitting. The eccentric swage nipple has offset centerlines that will maintain a flat side on the top or the bottom of the fitting, depending on how the fitting is rolled prior to installation.

Diverse swage nipples: concentric type (TBE, PBE, BBE), eccentric type (PBE, TBE, BBE). Material: ASTM A182 F316L; Surface Treatment: sandblasted.
Swage nipples are functionally similar to butt-welding reducers made in accordance with ASME B16.9, however, the most significant characteristic that distinguishes a swage nipple from a BW reducer is the diverse range of end connection configurations available with a swage nipple. These diverse end connection types include not only butt welding (BW) but also plain end (PE) and threaded end (TE), which will be discussed in later sections of this article. Moreover, the swage nipple is usually made by a hot or cold “swaging” process which results in enhanced strength and toughness. This makes swage nipples particularly useful in high-pressure and high-temperature applications where maintaining system integrity is critical.
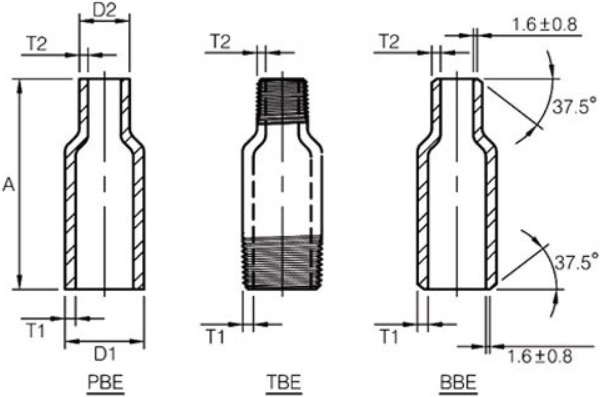
The technical drawing of concentric swage nipples with typlical end configurations of PBE, TBE and BBE.
Swage nipples can be used in screwed, socket-weld, or butt-weld connections. When used in these conditions, swage nipples will have different end connection preparations: (i) Screwed connection will require threaded ends (TE); (ii) Socket-weld connection requires plain ends (PE); (iii) butt-weld connection will have beveled ends (BE). Beveled and plain ends are generally furnished in accordance with ASME B16.25. Threaded ends may be furnished in accordance with NPT of ASME B1.20.1; BSPT of BS 21, BS EN10226-1, ISO 7-1; BSPP of BS 2779, BS EN228-1, ISO 7-1; or PT of GB/T 7306.
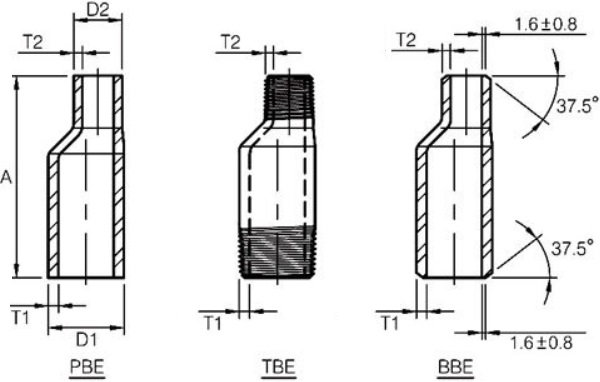
The technical drawing of eccentric swage nipples with typlical end configurations of PBE, TBE and BBE.
Since the swage nipple has a large-diameter end and a small-diameter end, there are nine configurations of end connections available: (1) TBE – threaded both ends; (2) BBE – beveled both ends; (3) PBE – plain both ends; (4) BLE/TSE – beveled large end and threaded small end; (5) PLE/TSE – plain large end and threaded small end; (6) TLE/BSE – threaded large end and beveled small end; (7) PLE/BSE – plain large end and beveled small end; (8) TLE/PSE – threaded large end and plain small end; (9) BLE/PSE: beveled large end and plain small end.
Swage nipples can be made from a wide range of metal materials covering: (1) mild carbon steels: ASTM A105, 20# Steel; (2) low-temperature steels: ASTM A350 LF2, LF6, ASTM A420 WPL6; (3) high strength low alloy steels: ASTM A694 F42, F46, F52, F60, F65, F70; (4) alloy steels: ASTM A182 F11, F5, F9, F91, F92; (5) austenitic stainless steels: ASTM A182 F304(L), F316(L), F304H, F316H, F309, F310, F317(L), F347, F44, F904L; (6) duplex stainless steels: ASTM A182 F51, F60, F53, F55; (7) special metals: Inconel 625, Incoloy 825, Alloy 20, Titanium Gr.2, Tantalum, Monel 400, Hastelloy C-276.

The swaging process for the fabrication of swaged nipples. The preheated round bar is fed into the swaging machine to reduce the diameter of one end.
Swage nipples may be machined from a forged bar or by a swaging process. Swaging is a manufacturing process used to produce swaged nipples by reducing the diameter of a metal tube or rod through a series of progressive steps. This process involves placing the workpiece into a swaging machine where it is subjected to high-pressure, radial hammering by dies. These dies compress the material uniformly around the circumference, forcing it to flow and take the shape of the die cavity. The process can be performed cold or hot, depending on the material and the desired properties of the final product. Swaging results in a finished part with enhanced mechanical properties, precise dimensions, and a smooth surface finish, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Swage nipples are available in sizes ranging from 1/4” to 12”, however, sizes no greater than 4” are most widely used in piping systems. The wall thicknesses may be furnished in accordance with ASME B36.10M and ASME B36.19M, or custom designed. You may click to view the detailed dimensions and weight of the swage nipples.
