Categories
- Pipe & Tube (18)
- Flange & Fitting (97)
- Fastener & Gasket (12)
- Valve & Pump (18)
- Base Material (11)
- Equipment (8)
- Application (30)
- Technical (110)
Ball valve is a kind of plug valve with a ball-shaped closure element. It can control the flow through it by using a hollow, perforated and pivoting ball. It is open when the ball’s hole is in line with the flow and closed when it is pivoted 90-degrees by the valve handle. The handle lies flat in alignment with the flow when open, and is perpendicular to it when closed, making for easy visual confirmation of the valve’s status.
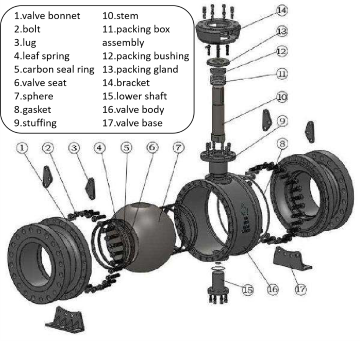
GA Drawings of Ball Valve
Ball valves can be designed and manufactured in accordance with a variety of major standards and Codes including ISO 7121 (Flanged and butt welded end steel ball valves), GB/T 12237 (General purpose industrial valves―flanged and butt-weld end steel ball valves), MSS-SP-72 (Ball valves with flanged or butt welding ends for general service), API 6D (Pipeline and piping valves), JPI-7S-48 (Flange connection ball valves), BS 5351 (Steel ball valves for the petroleum, petrochemical and allied industries), ASME B16.34 (Valves — Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End), etc.
Ball valves can be classified in many ways. One typical way to classify valves is according to its operation method. If the movement of the closure member is driven by the fluid flowing through the valve or its internal mechanism, such as in check valve and safety relief valve, the valve is called an automated valve or automatic valve. If the movement of the closure member is driven by an external actuator, such as handle lever, wheel, worm gear, or pneumatic/ hydraulic/ electric actuator, the valve is called an actuated valve.
Ball valves can also be classified according tonominal size: small-size valve (≤ DN 40); medium-size valve (DN 50 ~ DN 300); large-size valve (DN 350 ~ DN 1200); super large-size valve (≥ DN 1400). Ball valve classification according to nominal pressure: vacuum valve (< 1 standard atmosphere); low-pressure valve (≤ PN 1.6 MPa); medium-pressure valve (PN 2.5 MPa ~ PN 6.4 MPa); high-pressure valve (PN 10.0 MPa ~ PN 80.0 MPa); ultra-high-pressure valve (> 100 MPa). Ball valve classification according to working temperatures: high-temperature valves (T > 450°C); medium-temperature valves (120°C ≤ T ≤ 450°C); room-temperature valves (-29°C ≤ T < 120°C); low-temperature valves (-100°C ≤ T < -29°C); ultra-cryogenic valves (T < -100°C).
Ball valves classification according to the material they are made from: non-metallic valves such as PVC valve, ceramic valve; metal valves: cast iron valve, ductile cast iron valve, cast steel valve, copper alloy valve, nickel alloy valve, titanium alloy valve, stainless steel valve, alloy steel valve, forged steel valve; lined valves: lead-lined valve, PTFE-lined valve, ceramic-lined valve. Valve classification according to end connection types: flanged valves (RF or RTJ flanged); threaded valves (NPT or BSPT end); butt welding or socket welding valves; ferrule or grooved valves.
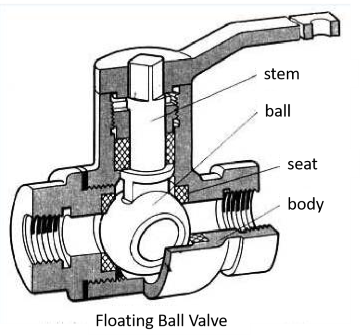
Ball valve can also be classified according to structure of the ball: The ball that floats is a floating ball valve, under the action of the medium pressure, the ball can produce a certain displacement and press on the sealing surface at the outlet end to ensure the outlet end seal; The ball that elastic is flexible ball valve, ball and seat sealing ring are made of metal materials, sealing pressure is very high, depending on the pressure of the medium itself has reached the requirements of sealing, must apply external force, this ball valve is suitable for high temperature and high pressure media; The ball that trunnion mounted is trunnion mounted ball valve, after compression does not produce movement, this valve has been widespread in severe service applications where pipeline flow may contain solids and harsh corrosives, operating at elevated temperatures and high pressures.
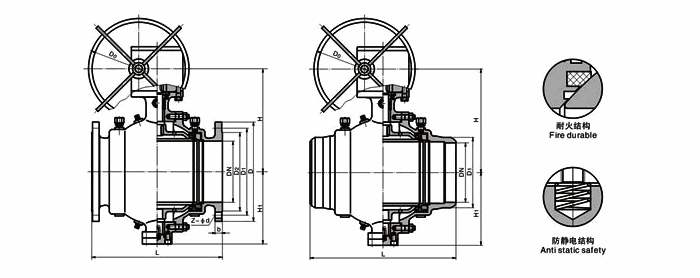
GA Drawings of Trunnion Mounted Ball Valve
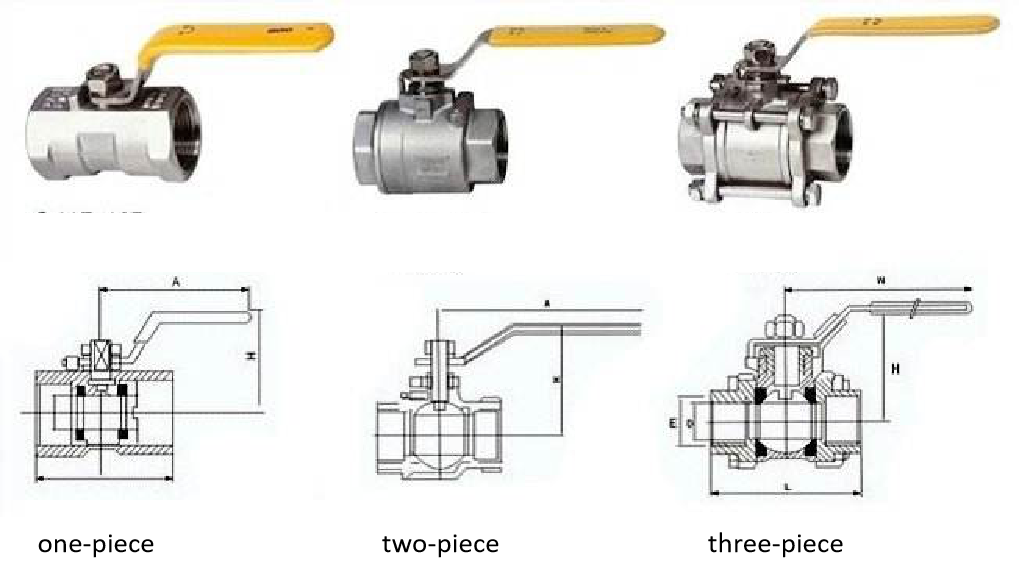
Ball valves classification according to the assembly structure, it can be divided in three commonly used designs: one-piece, two-piece and three-piece housings. The difference is how the ball valve is assembled:
One-piece —The valve parts are pressed or welded. The diameter of the ball is slightly smaller than that of the pipe. The valves can not be opened for cleaning or maintenance.
Two-piece — Two-piece ball valve is composed of two parts, the sealing effect is better than one-piece ball valve, the diameter of the ball and pipe diameter of the same, than one-piece ball valve easy to remove. Usually, the parts are connected via a threaded connection. The valve must be completely removed from the pipe in order to separate the two parts.
Three-piece — Three-piece ball valve is composed of three parts, valve cover and intermediate valve body, the parts are generally clamped together by bolt connections, it is easy to remove and maintain.
Ball valves classification according to the hole of the ball, such as reduced bore, full bore, and V-shaped.
Reduced bore — Most ball valves have a reduced bore. One-piece ball valves are almost always reduced bore.
Full bore — Full bore valves have the same bore diameter as the pipe. The advantage is that there is no additional friction loss and the system is mechanically easier to clean. The disadvantage is that the ball and the housing are bigger than a standard ball valve with reduced bore.
V-shaped — The hole in the ball or the valve seat has a “V” shaped profile, the required flow can be controlled more precisely by rotating the ball.
Ball valve can also be classified according to different number of ports. The valve may have two, three and four ports (2 way, 3 way or 4 way). The most of ball valves have two ports. The 3 way valves are designed to floating type and can be further categorized as L port and T port depending on the allowable flow directions passing through the passage. In the image below, you can see the different flows clearly.
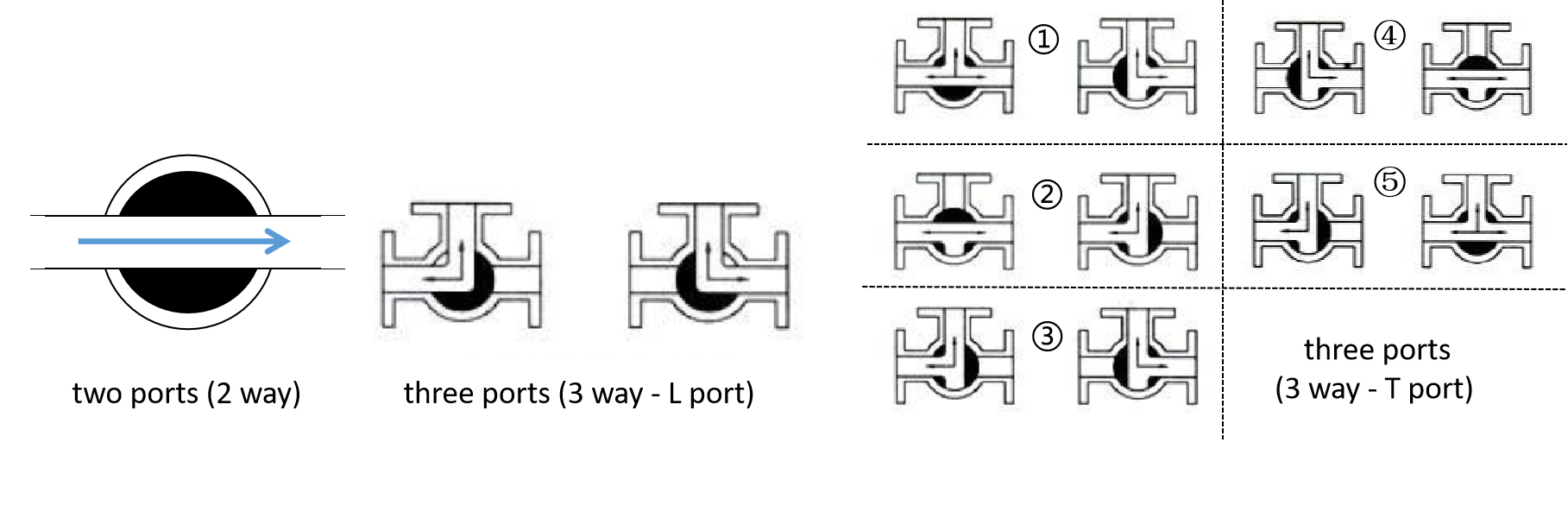
GA Drawings of different port fluids
